
Walailak Frontier 10, January 2019
Alu hypomethylation and type 2 DM
Diabetes mellitus, or DM, is a complex multifactorial disorder in which the person has high blood glucose (hyperglycemia). Type 2 DM is the most common type of diabetes. DM patients possess an increased risk of various geriatric conditions; therefore, type 2 DM is one of the most serious health problems in the world. Cellular senescence, particularly vascular senescence, is believed to be a main contributing factor to DM-related complications, such as retinopathy, kidney failure, cerebrovascular disease, and delayed wound healing. Nevertheless, the cellular senescence mechanism in DM remains to belargely unexplored. A low Alu methylation level, Aluhypomethylation, has been reported to represent a cellular senescence biomarker. Many studies concluded that genome-wide hypomethylationcan promotes genomic instability.
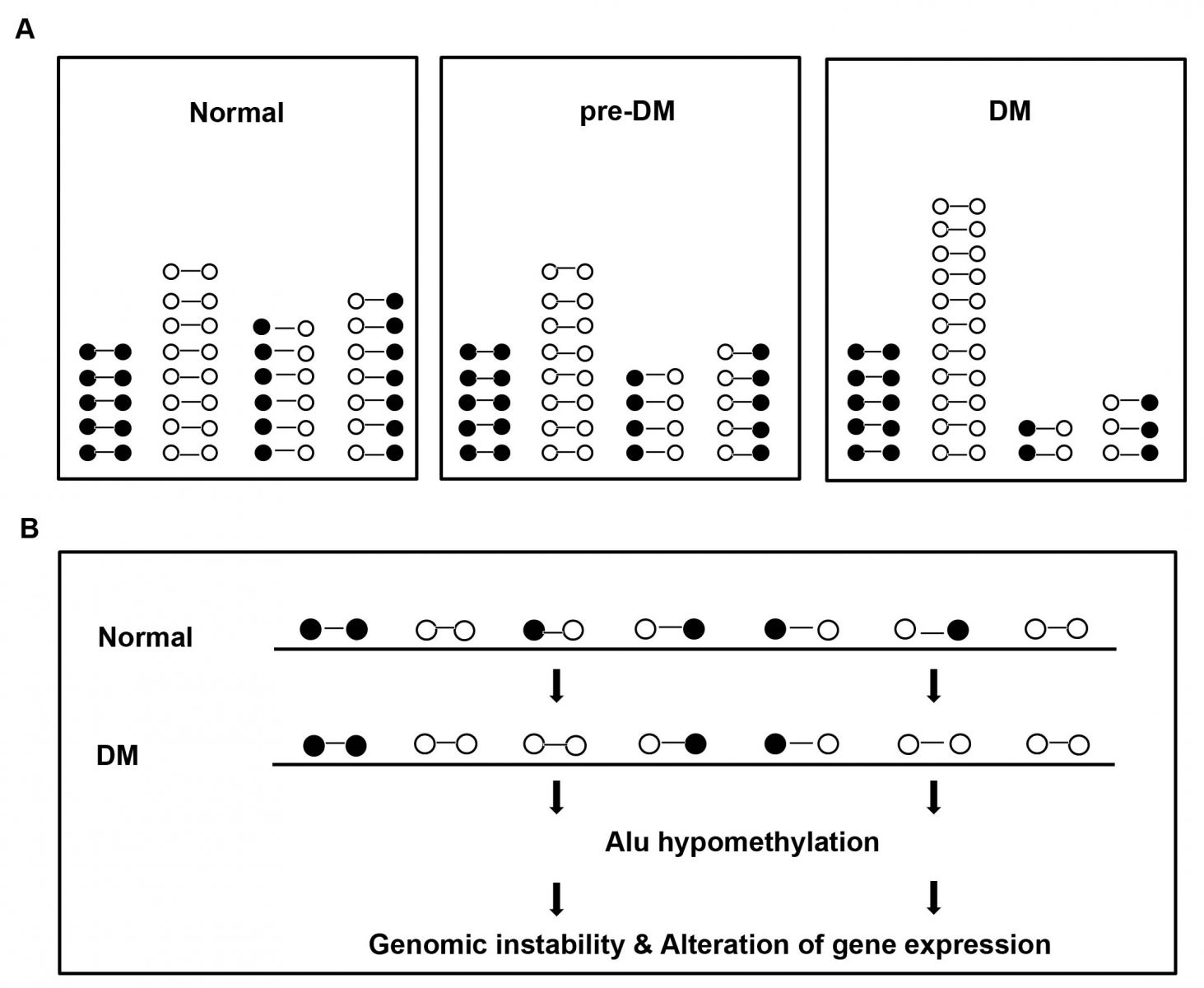
This study, we measured the level of Alu methylation in normal, pre-type 2 DM, and type 2 DM patients by ALU-Combined Bisulfite Restriction Analysis . We investigate Alu methylation levels of white blood cells of type 2 DM, pre-DM, and control . The DM group possess the lowest Alu methylation (P < 0.001, P < 0.0001 adjusted age ). In the DM group, Aluhypomethylation is directly correlated with high fasting blood sugar, HbA1C, and blood pressure. Therefore, genome-wide hypomethylation may be one of the underlining mechanisms causing genomic instability in type 2 DM. Moreover, Alu methylation levels may be a useful biomarker for monitoring cellular senescence in type 2 DM patients.
Sources:
Jirapan Thongsroy, Maturada Patchsung, Apiwat Mutirangura. 2017. The association between Alu hypomethylation and severity of type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, Clinical Epigenetics, 9:93
Facebook: wufrontovation
Related Link:
