
Walailak Frontier 19, August 2019
Thailand prospers with medicinal plants many of which have been successfully used to restore the Thais of a wide range of illness including the conditions related to the dysfunction of the central nervous system (CNS) such as anxiety, depression and dementia. Many Thai medicinal plants have been claimed to possess the CNS modulating effects including Apium graveolens L.
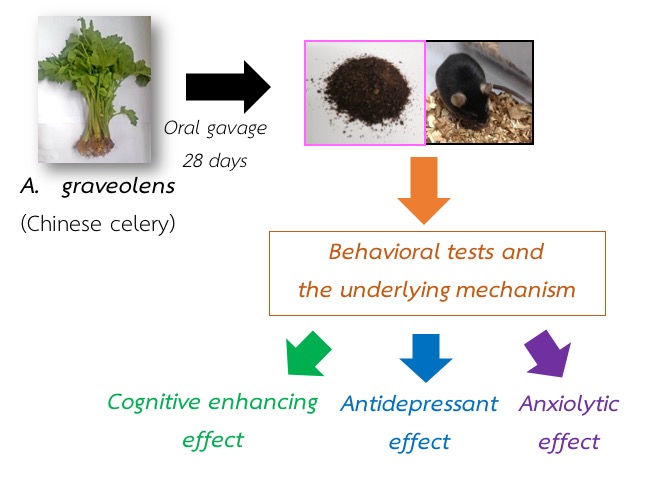
Chinese celery or A. graveolens, commonly known in Thailand as “Khuen chaai,” is a local herb of Eurasia, cultivated and consumed all over the world. Especially, their leaf stalks and seeds are utilized as a well-liked scented spice. In this study, A. graveolens at dose of 125-500 mg/kg body weight (BW) significantly improved all of anxiolytic-behavioral tests higher than the common anxiolytic drug such as diazepam, produced significant changes in antidepressant-behavior higher than the common antidepressant drug such as fluoxetine, and improved the cognitive enhancing behavioral tests higher than the common treatment for dementia such as donepezil. The underlying mechanism related to anxiolytic, antidepressant, and cognitive enhancing effects are the antioxidant activity and the specific neurotransmitter of the CNS.
Thailand prospers with medicinal plants many of which have been successfully used to restore the Thais of a wide range of illness including the condition which related to the dysfunction of the central nervous system (CNS) as anxiety, depression and dementia. Many Thai medicinal plants have been claimed to possess the CNS including the Apium graveolens L.
Chinese celery or A. graveolens, commonly known in Thailand as “Khuen chaai,” is a local of Eurasia, cultivated and consumed all over the world. Especially, their leaf stalks and seed are utilized as a well-liked scented spice. A. graveolens at dose of 125-500 mg/kg BW that were used in the study significantly improved all of anxiolytic- behavioral tests than the common anxiolytic drug use of diazepam, produced significant changes in antidepressant-behavior than the common antidepressant drug use of fluoxetine, and improved the cognitive enhancing behavioral tests than the common dementia drug use of donepezil treatment. The underlying mechanism-related to anxiolytic, antidepressant, and cognitive enhancing effects of A. graveolens are the antioxidant activity and the specific neurotransmitter of the CNS.
Sources:
Boonruamkaew, P., Sukketsiri, W., Panichayupakaranant, P., Kaewnam, W., Tanasawet, S., Tipmanee, V., Hutamekalin, P., Chonpathompikunlert, P., 2017. Apium graveolens extract influences mood and cognition in healthy mice. Journal of Natural Medicine. 71(3):492-505
Tanasawet, S., Boonruamkaew, P., Sukketsiri, W., Chonpathompikunlert, P., 2017. Anxiolytic and free radical scavenging potential of Chinese celery (Apium graveolens) extract in mice. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine. 7(1): 20-26
Boonruamkaew, P., Sukketsiri, W., Tanasawet, S., Chonpathompikunlert, P., 2015. Ameliorative Effect of Apium graveolens L. on Scopolamine-Induced Amnesia Mice. Isan Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, IJPS. 10(1): 82-93
Facebook: wufrontovation
Related Link:
